All introductory optics courses cover diffraction phenomena, and most begin their coverage of this topic with Fraunhofer diffraction. In Fraunhofer diffraction, the source and screen are arranged to be effectively at infinity from the diffraction device, a slit-like aperture, or a diffraction grating. This simplifies the treatment appreciably because the emitted waves reach the apertures as plane waves, all having the same phase and amplitude. We do away with these limitations in near-field, or Fresnel, diffraction, so named after the French engineer and physicist Augustin-Jean Fresnel (1788 – 1827). In this post, I provide a quick introduction to this phenomenon, with emphasis on the concepts of Fresnel zones and Fresnel integrals. Two solved examples are included along the way.
1. Obliquity factor
A crucial aspect of Fresnel diffraction is that waves emitted by a point source at a finite distance from an aperture or a straight-edge obstacle are spherical in nature. As light diffracts through the opening, points on the primary wavefront are envisioned as continuous emitters of secondary spherical wavelets; this is illustrated in Figure 1.
Figure 1. Near-field diffraction along an aperture.
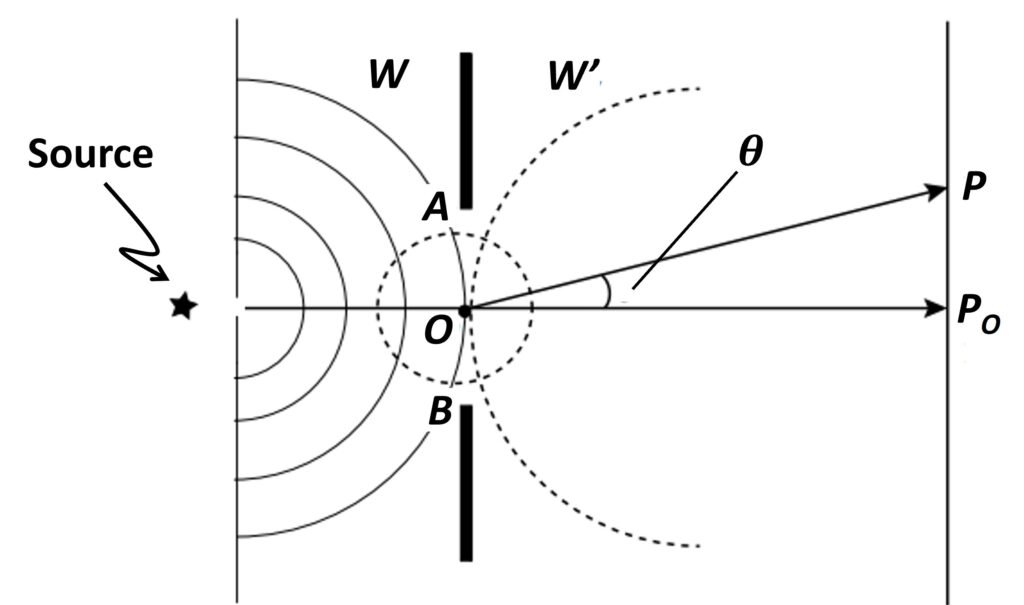
But if each wavelet radiated uniformly in all directions, in addition to generating an ongoing wave, there would also be a reverse wave travelling back toward the source. Since no such wave is found experimentally, we must somehow modify the radiation pattern of the secondary emitters. With this goal in mind, we introduce a quantity called the obliquity factor F():
In this equation, is the angle between a horizontal line through the secondary source and the line connecting it to the observation point (Fig. 1). The obliquity factor, when multiplied by the amplitude of a spherical secondary wavelet at the aperture, reduces it by a factor ranging from 1 to 0; the angle
= 0o is for the forward direction, and
= 180o is for the backward direction. Substituting
= 0o yields F(0o) = 1, which means that the obliquity factor has no effect on the amplitude of the forward wave. On the other hand, for
= 180o we obtain F(180o) = 0, so that multiplying this result by the wave amplitude yields zero, nullifying the backward-directed wavelets.
2. Basics of Fresnel diffraction
To develop a mathematical treatment of Fresnel diffraction, we refer to Figure 2, where arc WW represents a primary wave with a spherical wave front of radius emitted by a source S, and P is an observation point on the screen. In Figure 3, the arc W’W’ represents a wavelet of radius
emitted by a secondary source on the primary wave front at O. The line connecting S and P passing through the polar point O consists of the segments SO and OP, which are labelled
and
, respectively. Assuming that Eo is the amplitude at unit distance from the source, the disturbance per unit area of the aperture at a point of the wave front lying on the aperture can be described by
where t is time and is radial distance as designated in Figure 4; k and
are the wavenumber and angular frequency of the wave, respectively. Designating as t = 0 the instant when the wavefront is at the selected arbitrary point, the factor
would be unity and can be dropped from the expression above. The region impacted by the obliquity factor F(
) is
The wave in equation (3) propagates to a receiving point P as a secondary wavelet of an element of disturbance dEp given by
Combining equations (3) and (4) gives the disturbance at a point P due to the wavelets reaching P, that is,
To include contributions of all wavelets generated by the aperture points, we integrate over the area A:
Figure 2. Spherical wavefront emitted by a source, S.
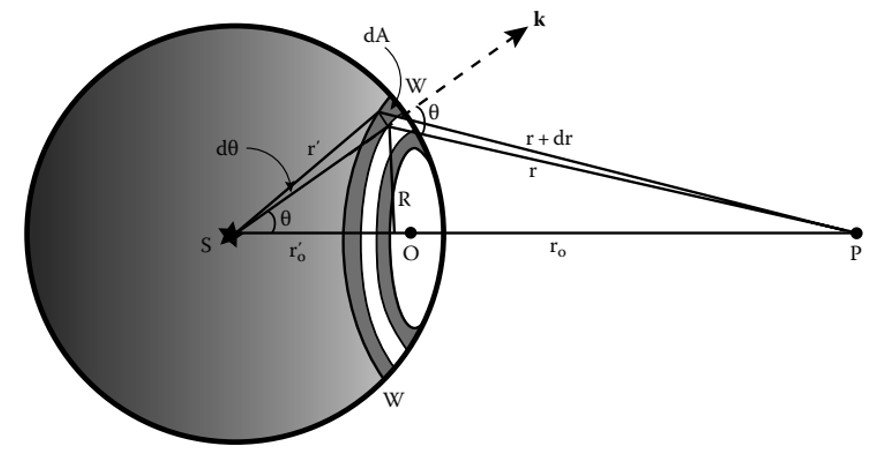
Figure 3. Path difference along SP and SMM’P.
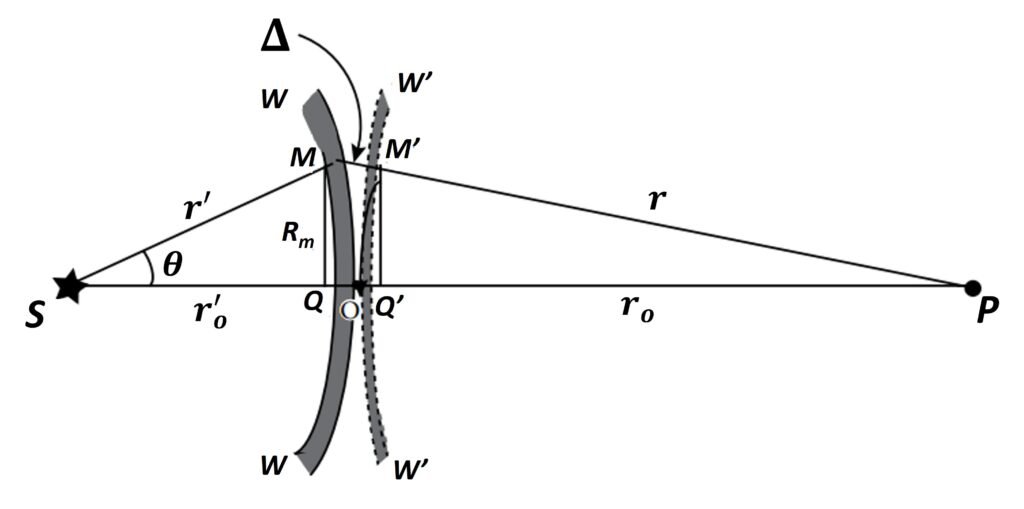
In an attempt to carry out the integration in (6), Fresnel introduced a special construction of the primary incident wave that encounters the apertures as it propagates. In his scheme, the incident wavefront is divided into zones of circles that have a finite width centered on the pole O. The circles are constructed such that the distance from the observation point P to the first (smallest) circle is r + /2; the distance from P to the second circle is r +
; the same pattern extends indefinitely, such that each circle is larger than the preceding one by
/2. The task then reduces to determining how many zones cross the aperture, counting the path differences and the corresponding phase differences for all wavelets reaching Pi, and ultimately adding the contributions to diffraction on the screen.
For a simple implementation of such a process, refer to Figure 3, in which we have a side view of an aperture, a segment of a Fresnel zone on a primary wave, and a wavelet generated at a point of the aperture. Consider the two points O and M through which the paths SOP and SMP pass. The first is the shortest path of light between the source and receiving point P traversed by the primary wave and the secondary wavelet generated at O. The second is the path OM plus that of a wavelet generated at M, another point on the primary wave. The two paths, being not equal, are of a path difference given by
which can be stated as
Segments QO and Q’O are known as the sagittas of the arcs WW and W’W’. For a small height of points M and M’ above the line SOP, these heights can be shown to equal
so that (8) becomes
But the path difference of a zone of order m is such that
Equating (10) and (11) and solving for Rm, (i.e., the value of R at the m-th order), we have
But, from the geometry of Figure 3, we also have
so that, equating (12) and (13) and manipulating,
But m/r0
1, hence the second term on the right-hand side of (14) can be dropped, giving
or
This equation indicates that the radius of a given Fresnel zone is proportional to the square root of its order m. For an aperture of radius a, whose center is on the line connecting the source and the observation point P, the number of zones N that pass through the aperture can be calculated as
where Am is the area of the m-th zone. Letting the central zone (the first zone) be labelled m = 1, we have A1 = , so the number N of zones that would fit into the aperture is
Number N may be used to distinguish Fraunhofer diffraction from Fresnel diffraction: if N 1, Fraunhofer diffraction dominates; for N > 1, Fresnel diffraction holds.
Example 1
Consider a monochromatic light of wavelength = 680.0 nm incident on an aperture of radius a = 8.0 mm. The aperture was situated in the middle between the source and a point P on the screen along the line SOP. For S and P to be 25 cm apart, find:
(a) The radius of the central zone.
(b) The number of Fresnel zones that would be accommodated through the aperture.
Solution, Part a. We have m = 1, = 0.008 m,
= 0.008 m, and
= 680
10‒9 m, so that, substituting into (12),
Part b. The number N of Fresnel zones that would pass through the aperture is given by equation (17),
4. Fresnel diffraction in a rectangular aperture – Analytical treatment
We now turn to an analytical treatment of Fresnel diffraction for a rectangular aperture. As shown in Figure 4, we begin by taking an elemental strip chosen along the width W of the rectangular aperture. A spherical wave incident on a very large number of these strips would constitute a problem in requiring the phase at all points of the strip to be constant; harder still would be to require the phase to be the same along successive elemental strips. One way to remedy this is to have a cylindrical source parallel to the aperture plane, so that all points of the cylindrical wave front would have the same phase. Aside from the geometry of the aperture, which requires the source to be an extended slit so that cylindrical waves are considered, no constraints are applied and the Fresnel equation (6) can be restated as
where all constants are gleaned into a parameter C1. We assume that the surface integral over a closed surface including the aperture is zero everywhere except over the aperture itself, so that we need perform the integration only over the aperture in the yz-plane of Figure 4a. A side view, which shows the curvature of the cylindrical wavefront, is drawn in Figure 4b.
Figure 4. (a) Cylindrical wavefronts from source slit S are diffracted by a rectangular aperture. (b) Edge view of (a).
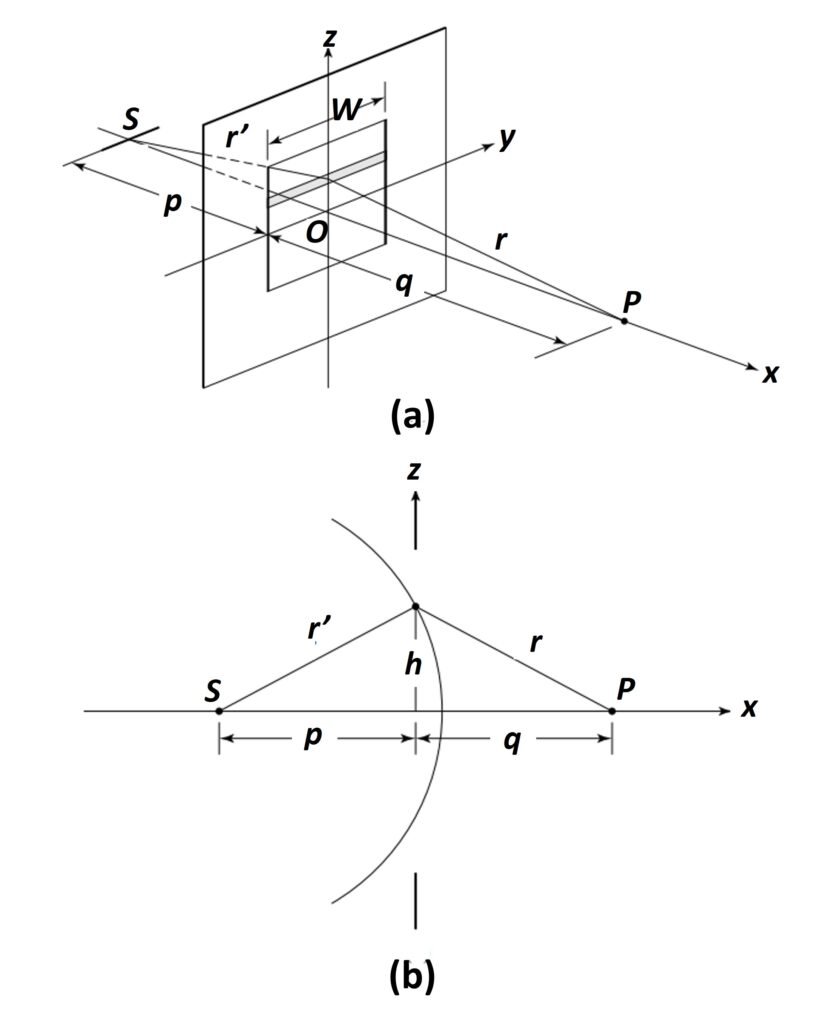
The distance r + r’ may be determined approximately from this figure. For h p and h
q, a binomial expansion approximation gives
so that
Proceeding similarly with r,
Adding the two foregoing results,
For convenience, we introduce the variables
and
so that
If the elemental area dA is taken to be the shaded strip in Figure 4, dA = Wdz, h = z, and
The exponent in the integrand can be restated as
where k is wavenumber and is the wavelength. Making a change of variable, we let
or
so we can restate (25) as
where Ap is a complex scale factor with dimensions of electric field amplitude. Using Euler’s theorem on the integrand, it follows that
The two integrals on the right-hand side are known as Fresnel integrals, and are routinely denoted with the simplified notations
and
Substituting these into (29) gives
Now, note that the irradiance at P is given by
where is vacuum permittivity, c
3.0
108 m/s, and Ep is electric field intensity, Replacing EP from (31) brings to
where we have introduced the irradiance scale factor , namely
It is important to note that C(v) and S(v) are both odd functions, so that
The choice of v in the Fresnel integrals is determined by the vertical dimensions of the diffraction aperture.
Some values of the Fresnel integrals are listed here. Tabulated values are convenient, but often require tedious interpolation. A better alternative is to use software such as Mathematica or MATLAB, or resort to this free web-based app by Casio.
5. The Cornu spiral
If the values of the Fresnel integrals are plotted with C(v) on the horizontal axis and S(v) on the vertical axis, the resulting graph is the so-called Cornu spiral, Figure 5. The origin v = 0 of the Cornu spiral corresponds to z = 0 and therefore to the y-axis through the aperture of Figure 4. The top part of the spiral (z > 0 and v > 0) represents contributions from strips of the aperture above the y-axis, and the twin spiral below (z < 0 and v < 0) represents similar contributions from below the y-axis. The two limit points or “eyes” of the spiral at E and E’ represent linear zones at z = .
Furthermore, variable v, introduced in (27.2), represents the length along the Cornu spiral itself. To see this, recall that the incremental length dl along a curve in the xy-plane is given by the Pythagorean relationship
But in the Cornu spiral plane the x– and y-coordinates are given by the Fresnel integrals C(v) and S(v), respectively, giving
Another noteworthy feature of the Cornu spiral is that its tangent at a certain point (x, y) is given by the tangent of variable /2 at that particular point:
Figure 5. A Cornu spiral.

6. Unobstructed wavefront
The irradiance in the Fresnel diffraction pattern associated with different apertures are often compared to the irradiance Iu associated with an unobstructed wavefront. An unobstructed wavefront is modeled by passage through an aperture with a vertical dimension 2 that ranges from ‒∞ to +∞. In this case, the total irradiance Iu at point P is proportional to the square of the length of the phasor drawn from E’ to E in Figure 5. These limiting points have coordinates (C(v2), S(v2)) = (0.5, 0.5) and (C(v1), S(v1)) = (‒0.5, ‒0.5), as given by the improper integrals
and from the fact that C(v) and S(v) are odd functions. It follows that, substituting into (33), the unobstructed irradiance becomes
Other irradiances may be compared conveniently to this result.
Example 2
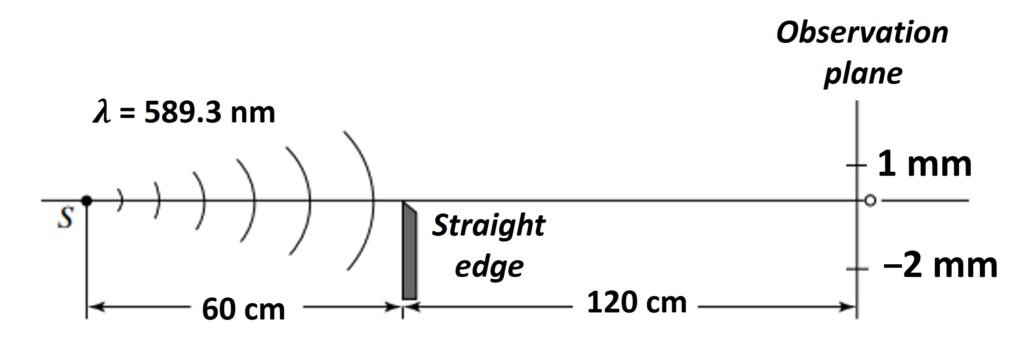
A slit illuminated with sodium light ( = 589.3 nm) is placed 60 cm from a straight edge and the diffraction pattern is observed using a photoelectric cell, 120 cm beyond the straight edge. Determine the irradiance at (a) 2 mm inside and (b) 1 mm outside the edge of the geometrical shadow.
Solution, Part a. For either position, parameter L is such that (equation (23))
Let z’ be the coordinate of the point O’ in the aperture plane along the straight line from S to the observation point P (see Figure 2). In the case at hand, with y = ‒2 mm, we may write
The values of the z1 and z2 that mark the edges of the unobstructed regions in the aperture plane are to be measured relative to this point, so z2 = ∞ and z1 = +6.6710‒4 m. We proceed to compute the modified variables v1 and v2:
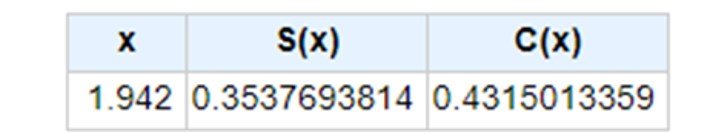
The Fresnel integrals for v2 are obvious: C(v2) = S(v2) = 0.5. In turn, entering v1 into the Casio app gives C(v1) = 0.4315 and S(v1) = 0.3538, as shown.
Referring to eq. (29), we compute the relative irradiance I:
Comparing this with the unobstructed irradiance as given by (39), we get
Solution, Part b. In this case, z’ becomes
so that z2 = ∞ and z1 = ‒3.3310‒4 m, updating v2 and v1,
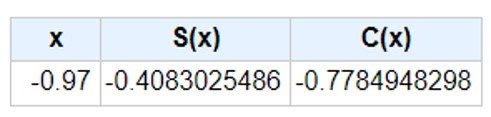
As before, the Fresnel integrals for v2 are C(v2) = S(v2) = 0.5. Next, entering v1 into the Casio calculator gives C(v1) = ‒0.7785 and S(v1) = ‒0.4083, as shown.
The relative irradiance then becomes
References
- HAIJA, A.I., NUMAN, M.Z. and FREEMAN, W.L. (2018). Concise Optics: Concepts, Examples, and Problems. Boca Raton: CRC Press.
- HECHT, E. (2017). Optics. 5th edition. Upper Saddle River: Pearson.
- PEDROTTI, F.L., PEDROTTI, L.M. and PEDROTTI, L.S. (2006). Introduction to Optics. 3rd edition. Boston: Addison-Wesley.




